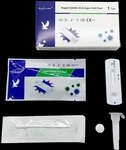
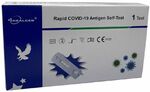
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The disease was first identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China, and has since spread globally, resulting in the 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic. Common symptoms include fever, cough and shortness of breath. Muscle pain, sputum production and sore throat are less common. While the majority of cases result in mild symptoms, some progress to pneumonia and multi-organ failure. The deaths per number of diagnosed cases is estimated at 3.4% but varies by age and other health conditions. This percentage does not reflect undetected cases.The infection is typically spread from one person to another via respiratory droplets produced during coughing and sneezing. Time from exposure to onset of symptoms is generally between two and 14 days, with an average of five days. The standard method of diagnosis is by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) from a nasopharyngeal swab or throat swab. The infection can also be diagnosed from a combination of symptoms, risk factors and a chest CT scan showing features of pneumonia.Recommended measures to prevent the disease include frequent hand washing, maintaining distance from others, and not touching one's face. The use of masks is recommended for those who suspect they have the virus and their caregivers but not the general public. There is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for COVID-19. Management involves treatment of symptoms, supportive care, isolation and experimental measures.The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the 2019–20 coronavirus outbreak a pandemic and a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). Evidence of local transmission of the disease has been found in many countries across all six WHO regions.







![[AKL] Free - Board an Airnz Dreamliner, Get Vaccinated in Business Class, Free Snacks in Economy at Auckland Airport](https://files.cheapies.nz/n/97/29997.jpg?h=21eda00a)



![[Android & iOS] Free 2 Months of BitGym Premium (Virtual Tours for Workouts) (Was $9.99/Month)](https://files.cheapies.nz/n/49/23149.jpg?h=58426365)
![[Wellington] Park Hotel from $1 a Night - 'pay as Much as You Can Afford' for Wellingtonians Who Have Had Travel Plans Cancelled](https://files.cheapies.nz/n/44/22944.jpg?h=4d50a60c)